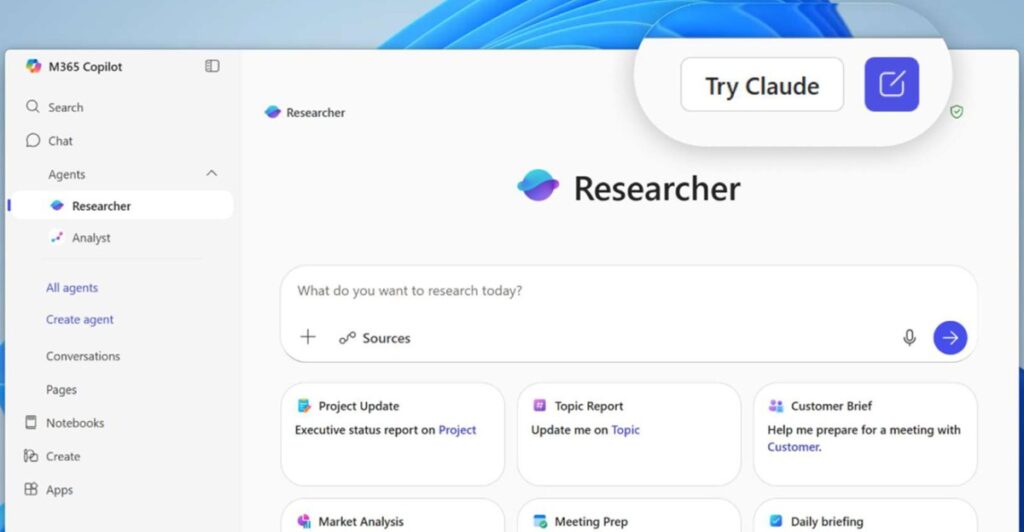
In a significant move that enhances its Microsoft 365 Copilot offering, Microsoft has integrated Anthropic’s AI models, Claude Sonnet 4 and Claude Opus 4.1. This development expands the toolset for businesses, providing not only AI-driven assistance but also an essential versatility in choosing the optimal model for various tasks. Historically, Microsoft has relied almost exclusively on OpenAI’s technology within its ecosystem, but this shift signifies a diversifying strategy that increases choice and functionality for users.
The integration of Anthropic models will be particularly impactful in Microsoft 365 Copilot’s Researcher and Copilot Studio, offering users the ability to switch between OpenAI and Anthropic systems seamlessly. This user-friendly approach aims to enhance productivity by allowing businesses to leverage the strengths of both models depending on their specific needs. For instance, Claude Opus 4.1, known for its advanced reasoning capabilities, could outperform OpenAI’s offerings in complex problem-solving scenarios, particularly those requiring a nuanced understanding of context and task flow.
From a comparative analysis perspective, both platforms showcase distinct strengths and weaknesses. OpenAI has set the standard in generative AI, promoting significant milestones in natural language processing and user interaction. However, Anthropic’s models, notably Claude Sonnet 4 and Claude Opus 4.1, emphasize safety and cognitive safety protocols. This focus on ethical AI could resonate with businesses prioritizing responsible use of technology—particularly in industries sensitive to data security and regulatory compliance.
Cost and return on investment (ROI) are crucial considerations when evaluating competing platforms. While detailed pricing structures are often proprietary, businesses can expect to see variance in costs associated with model usage tiers, Cloud infrastructure, and licensing fees. Historically, OpenAI models have positioned themselves at a competitive price point, though their reliance on a singular model set can restrict flexibility. In contrast, Anthropic’s introduction into the marketplace may generate a more competitive pricing landscape, particularly for enterprises that require scalable solutions to harness AI in diverse workflows.
Scalability is an essential factor as organizations pursue digital transformation. Microsoft’s decision to host Anthropic’s models on Amazon Web Services, a competitor to its Azure Cloud platform, highlights the practical realities of cloud service ecosystems. While this may sound contradictory, it reflects a broader trend where companies prioritize functionality and service reliability over allegiance to a single platform. With tools like Microsoft Copilot Studio, businesses can expect robust scalability, enabling them to manage a mix of models—both Anthropic and OpenAI—tailored for specific tasks, thus allowing them to scale operations efficiently without sacrificing model performance or reliability.
Moreover, Microsoft’s expanding integration of Anthropic’s AI into tools such as Excel and PowerPoint indicates a commitment to enhancing the user experience based on performance outcomes. By iterating based on actual user data and feedback, Microsoft aims to ensure that its offerings not only keep pace with market expectations but actively drive efficiencies in how businesses leverage AI within their workflows.
The broader implications of this strategic pivot stretch beyond mere model integration. Microsoft’s collaborations reflect an emergent trend through which companies are increasingly prioritizing adaptability in the face of rapid technological advancements. Such developments underscore a necessity for businesses to regularly evaluate their AI-automation strategies. The competition between leading platforms like OpenAI and Anthropic will likely spur further innovations, ultimately benefiting end-users who demand more efficiency and effectiveness from digital tools.
As leaders in small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) consider their AI strategies, it is essential to examine the potential benefits of flexibility offered by platforms like Microsoft’s 365 Copilot, particularly in collaboration with Anthropic models. This can mean a more tailored approach to automation that aligns closely with specific operational goals, boosting productivity and deeply personalizing user experiences. The decision to adopt either platform should focus not merely on cost analysis but also on potential impacts on workflow, company culture, and long-term strategic goals.
FlowMind AI Insight: The integration of Anthropic’s models into Microsoft 365 Copilot exemplifies the industry’s shift towards adaptable, user-centric AI solutions. As companies navigate this evolving landscape, prioritizing flexibility and ethical considerations can yield substantial competitive advantages. The choice of an AI partner will likely define the trajectory of an organization’s digital transformation journey.
Original article: Read here
2025-09-24 15:00:00