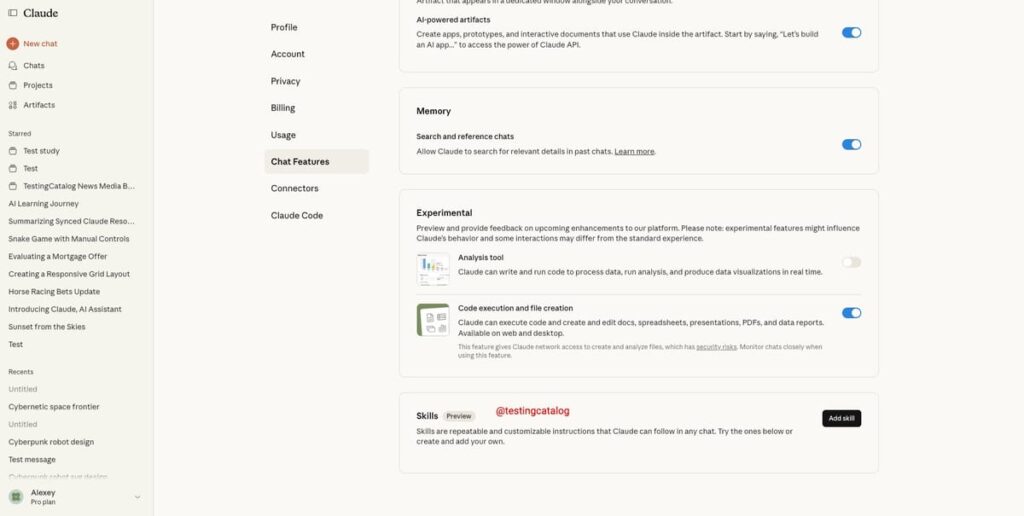
Anthropic has strategically positioned itself to enhance the Claude platform by introducing a promising feature referred to as Skills. This addition allows users to upload customizable and repeatable instructions, termed skills, through either a .skill file or a zipped folder that contains a SKILL.md file. This initiative underscores the company’s efforts to formalize a file-based standard for user-defined capabilities, potentially paralleling existing functionalities in established AI tools, such as Dia Browser, which provides similar user-activated custom functions.
The primary target audience for this new feature includes power users, developers, and even those with a desire for refined control over Claude’s outputs. Previously, users had limited options that mostly revolved around style selectors, lacking true custom prompt functionalities. The introduction of Skills is set to facilitate more nuanced workflow automations. It may empower users to execute a range of tasks, such as data transformations, content generation, and triggering domain-specific tasks through easily manageable keywords. For example, individuals engaged in tasks such as SVG Robot benchmarking or data extraction could benefit immensely by scripting their own skills. This capability would significantly reduce the reliance on prompt engineering for each individual task, which often proves cumbersome and time-consuming.
However, despite its potential, Anthropic has yet to clarify the specific types of tasks or automations that Skills will enable or provide public samples for users to evaluate. There is also no designated timeline for a formal launch. The Skills feature currently resides within Claude’s settings, indicating the likelihood of mainstream availability across different user tiers, contingent upon a successful initial testing phase. The company has also been making strides in real-time UI generation and enhancing modularity in Claude’s web interface, which suggests that Skills might evolve beyond mere text-based instructions into more interactive or artifact-generating add-ons. This aligns with Anthropic’s broader intent to make Claude a more versatile tool for both technical and non-technical users, which is essential to compete with industry players like OpenAI.
When comparing Claude and its Skills feature to platforms like OpenAI, a notable distinction emerges in their approach to user customization and flexibility. OpenAI has already established a reputation for offering robust plug-in and custom function support, which provides users with significant latitude in how they apply AI capabilities to their workflows. This was a critical factor for enterprises seeking to maximize the return on investment when integrating AI solutions. Consequently, as organizations evaluate the potential of these competing platforms, they will need to consider both the direct capabilities and the long-term scalability that each solution offers.
In contrast, while Claude’s introduction of Skills signifies a positive step towards empowering users with equally robust customization options, there remains an evaluative gap regarding its direct applicability and user experience in real-world scenarios. The level of documentation, community support, and user case examples will be pivotal in determining its effectiveness and adoption rate among SMBs. Thus, while the potential advantages appear promising, the practical execution will determine Claude’s ROI for users and its capacity to scale within diverse business contexts.
Moreover, as businesses navigate the complexities of automation tools like Make and Zapier, each offers its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Make provides more intricate scenarios with advanced logic and multi-step automations, which can be markedly beneficial for complex tasks and specialized workflows. On the other hand, Zapier is favored for its extensive integrations and user-friendly interface, making it a go-to for businesses seeking quick and straightforward setups. The cost structures of these platforms also warrant attention, as they vary widely and can impact the ROI calculations for different user groups.
Ultimately, the decision for SMB leaders and automation specialists to invest in any of these platforms—be it Claude with its forthcoming Skills, OpenAI, Make, or Zapier—must be rooted in an analytical assessment of each tool’s strengths in addressing specific business needs. Factors such as task complexity, user experience, integration capabilities, and cost efficiency should serve as vital touchpoints in the decision-making process.
In conclusion, the potential introduction of Skills in Claude represents a significant opportunity for Anthropic to bridge the gap in customizable AI functionalities. As the competitive landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain attuned to the developments in this space and weigh their options judiciously based on empirical evaluations. Given the burgeoning need for automation and AI integration, businesses that adopt a proactive and analytical approach to these evolving tools can unlock substantial value.
FlowMind AI Insight: As AI platforms advance, personalized and customizable functionalities will increasingly determine their adoption in business environments. SMB leaders must prioritize thorough assessments of these features to enhance operational efficiencies and drive scalable growth.
Original article: Read here
2025-10-01 15:45:00